Run commands – the secret shortcuts of the Windows Operating System – are an incredibly efficient way to access various system utilities and functions without having to click through numerous menus and tabs. While they may seem intimidating to the uninitiated, they’re actually quite simple to use once you understand their basics. And the best part? They’re a real time-saver.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of Windows Run commands. Whether you’re an experienced power user looking to brush up on your skills or a novice venturing into the heart of your OS, you’ll find value here. We’ve categorized popular Run commands into easy-to-digest sections, each complete with a handy table for quick reference. By the end, you’ll have an arsenal of tools to navigate your Windows system with ease and efficiency.

Table of Contents
What are Run Commands?
As we kickstart this fascinating journey, you might be asking yourself, “What exactly are Run commands?” Don’t worry; we’ve got you covered!
Run commands are essentially shortcuts that allow you to access applications, files, and operating system functions in Windows without navigating through a maze of windows and menus. These commands can be entered into the ‘Run’ dialog box that is easily accessible on your system. Think of them as the ‘secret passageways’ in a giant castle that is your Windows Operating System. They provide a swift and direct path to your destination, saving you a significant amount of time.
The Run Dialog Box
Accessing the Run dialog box is a breeze. There are two easy methods you can use.
- First, you can press the Windows logo key + R on your keyboard. This hotkey combination is like your express elevator to the Run command world. \
- You can click on the ‘Start’ button, scroll through the apps, find ‘Windows System,’ expand it, and click on ‘Run.’ The Run dialog box should now be displayed on your screen.

The Run dialog box is rather simple, boasting a minimalist design with only a text box and three buttons. The text box is where you’ll enter your commands. Once you’re ready, hit ‘OK,’ or press Enter to execute them.
To demonstrate, let’s revisit our Microsoft Word example from earlier. Type ‘winword’ into the text box and press Enter. Voila! Microsoft Word springs to life on your screen, all thanks to a quick Run command.
One important feature of the Run dialog box is its memory. It remembers the commands you’ve previously entered, allowing you to easily access and reuse them. Simply click on the dropdown arrow to the right of the text box to see your command history.
Essential Windows Run Commands
Alright, tech adventurers! Now that we’ve familiarized ourselves with the Run dialog box, it’s time to delve into the essence of our guide – the Run commands themselves. This section is all about essential Run commands that every Windows user, from beginners to seasoned power users, can benefit from.
Before we go any further, here’s a handy table listing these commands and their functions for your quick reference:
| Run Command | Description |
|---|---|
| calc | Opens the Calculator |
| cmd | Opens Command Prompt |
| control | Opens Control Panel |
| mspaint | Opens Microsoft Paint |
| notepad | Opens Notepad |
| winword | Opens Microsoft Word |
| excel | Opens Microsoft Excel |
| powerpnt | Opens Microsoft PowerPoint |
| taskmgr | Opens Task Manager |
| explorer | Opens Windows File Explorer |
| regedit | Opens Registry Editor |
| fsquirt | Bluetooth Transfer Wizard |
| certmgr.msc | Certificate Manager |
| main.cpl | Mouse Properties |
| mstsc | Remote Desktop |
| mmsys.cpl | Sounds and Audio |
| powershell | Windows PowerShell |
| mblctr | Windows Mobility Center |
| magnify | Magnifier tool |
Now, let’s delve deeper into some of these commands:
calc: Have you ever needed to make quick calculations while working on a project? Just type ‘calc’ in the Run dialog box, and the Calculator app will open up, ready to crunch those numbers.
cmd: If you’re a fan of text-based interfaces, this command is for you. Typing ‘cmd’ opens the Command Prompt, a more powerful cousin of the Run dialog box. From here, you can interact with your system using a wide array of commands and scripts.
notepad: Need to jot down notes or write code quickly? Just type ‘notepad’ to open the trusty Notepad application, a staple of every Windows system.
taskmgr: If your computer is running slow, or an application isn’t responding, type ‘taskmgr’ to open the Task Manager. Here, you can view and manage currently running applications and processes.
explorer: Want to browse your files? The ‘explorer’ command opens the Windows File Explorer, providing a graphical interface for viewing and managing your files and folders.
regedit: This command opens the Registry Editor, a powerful tool that provides access to the registry database where Windows and many applications store their configurations. Remember, making incorrect changes here can harm your system, so be sure to know what you’re doing.
mblctr: This command opens the Windows Mobility Center, which provides quick access to the most commonly used mobile PC settings, like brightness, volume, or battery status.
Windows System Configuration Run Commands
With the basics in your toolbox, let’s step further into the world of Run commands. This section focuses on commands related to system configuration. These commands are perfect for power users and those who like to tinker with their system settings, but they’re also handy for anyone looking to troubleshoot issues or adjust their system’s behavior.
Here’s a table summarizing the commands we’ll discuss in this section:
| Run Command | Description |
|---|---|
| appwiz.cpl | Opens the Programs and Features panel |
| compmgmt.msc | Opens Computer Management |
| control printers | Opens the Devices and Printers panel |
| desk.cpl | Opens Display Settings |
| devmgmt.msc | Opens Device Manager |
| diskmgmt.msc | Opens Disk Management |
| firewall.cpl | Opens Windows Defender Firewall |
| inetcpl.cpl | Opens Internet Properties |
| intl.cpl | Opens Region Settings |
| powercfg.cpl | Opens Power Options |
| sysdm.cpl | Opens System Properties |
| wmimgmt.msc | Opens WMI Control (Windows Management Instrumentation) |
| hdwwiz.cpl | Opens the “Add Hardware Wizard” |
| desk.cpl | Display Properties |
| timedate.cpl | Date and Time Properties window |
| printmanagement.msc | Print Management console |
Let’s walk through some of these:
appwiz.cpl: Remember how frustrating it can be to uninstall a program using the traditional way? Type ‘appwiz.cpl,’ and you’ll get a list of all programs installed on your computer, making the uninstallation process just a few clicks away.
compmgmt.msc: This command opens the Computer Management console. This tool helps you manage your system’s drives, users and groups, services, and system tools, all under one roof.
control printers: If you frequently print documents, ‘control printers’ is a command you’ll love. It directly opens the Devices and Printers panel, allowing you to manage your printing and scanning devices efficiently.
devmgmt.msc: If you’re experiencing issues with a device, or want to update a driver, type ‘devmgmt.msc’ to open the Device Manager. This tool provides a detailed view of all the hardware installed on your system, enabling you to manage drivers and troubleshoot device issues.
sysdm.cpl: To quickly access system properties, use ‘sysdm.cpl’. This command will take you to a hub of system settings, including Computer Name, Hardware, Advanced, and System Protection tabs.
firewall.cpl: This command opens the Windows Defender Firewall. If you’re troubleshooting network connectivity issues or want to modify your system’s firewall settings, this command is a great starting point.

printmanagement.msc: This command opens the Print Management console, which allows you to view and manage all the print servers in your network.
As with the previous set of commands, these are very powerful and can greatly influence your system’s behavior, so always use them with caution. Always ensure you fully understand a command and its implications before running it.
Networking and Internet Run Commands
Stepping away from system configurations, let’s now venture into the realm of networking and internet-related Run commands. These commands come in handy for anyone looking to troubleshoot network issues, access network settings quickly, or get detailed network information.
Below, you’ll find a summary table for your convenience:
| Run Command | Description |
|---|---|
| cmd /k ipconfig | Displays the IP configuration |
| cmd /k ping www.google.com | Pings www.google.com and displays results |
| control netconnections | Opens Network Connections |
| inetcpl.cpl | Opens Internet Properties |
| nslookup www.google.com | Looks up the IP address of www.google.com |
| cmd /k tracert www.google.com | Traces and displays the path that a packet takes to reach www.google.com |
| ncpa.cpl | Opens Network Connections |
| cmd /k net view | Displays the list of computers in your current network |
| fsmgmt.msc | Shared Folders |
| shrpubw | Opens the Create a Shared Folder Wizard |
Now, let’s take a closer look at a few of these commands:
cmd /k ipconfig: When troubleshooting network issues, your IP configuration is often the first place to check. This command opens the Command Prompt and runs ‘ipconfig,’ displaying your system’s IP configuration, including your IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
cmd /k ping www.google.com: If you’re having trouble accessing a website, you might want to check if the site is reachable from your network. This command pings www.google.com and displays the results. You can replace www.google.com with any other website you’re trying to reach.
control netconnections or ncpa.cpl: Need to access your network connections quickly? Either of these commands will take you straight to the Network Connections panel, where you can view and manage your network connections.
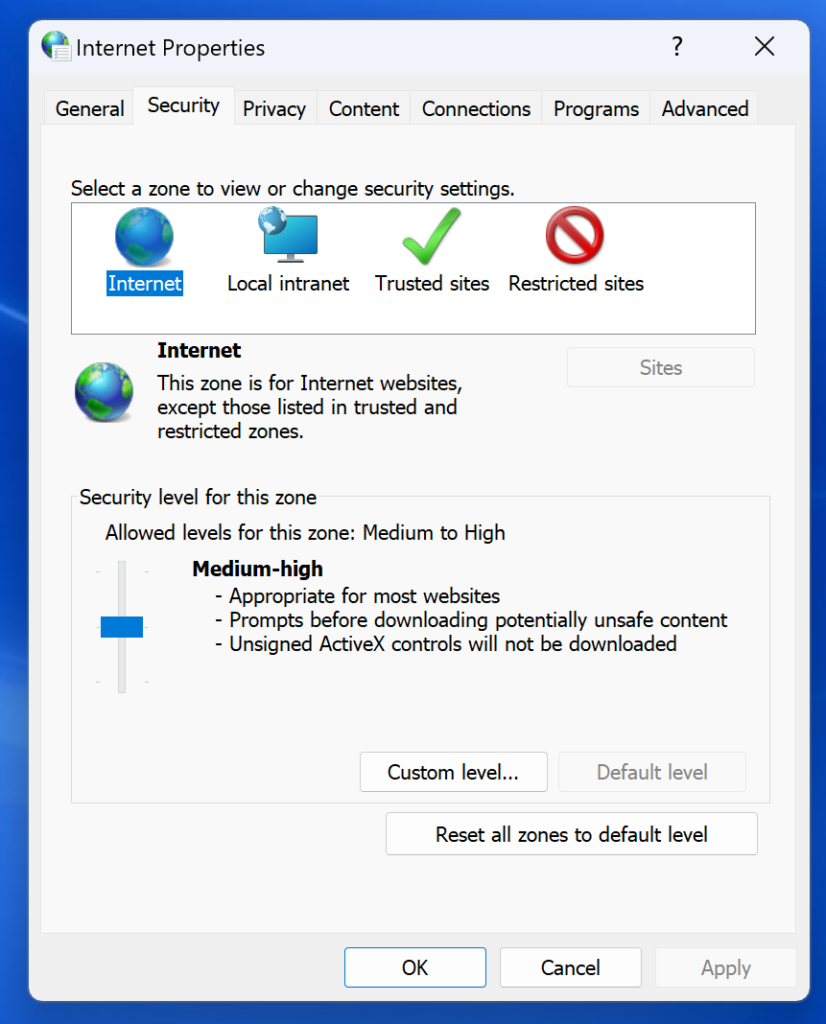
inetcpl.cpl: This command opens the Internet Properties dialog, where you can adjust your internet settings, including browsing history, security settings, and more.
nslookup www.google.com: Need to find the IP address associated with a website? ‘nslookup’ followed by the website URL will give you that information.
cmd /k tracert www.google.com: If you’re experiencing slow or interrupted access to a website, this command can help identify where the issue lies. It traces and displays the path that a packet takes to reach the website, showing each ‘hop’ along the way.
These commands will equip you with the basic tools you need to understand your network and troubleshoot common issues. However, it’s important to note that while these commands can help diagnose problems, they won’t necessarily fix them. In some cases, you might need to delve deeper into your network settings or contact your ISP for further assistance.
Always keep in mind that these commands, while powerful, are tools to aid your understanding and efficiency. They should be used responsibly and with a clear understanding of their function and potential effects.
Run Commands for System Tools
Next up, we’re going to navigate the fascinating world of system tools Run commands. These commands are time-saving shortcuts to essential system tools and utilities that you might need to access frequently. System tools Run commands can make troubleshooting, managing system settings, and customizing your Windows experience much easier.
Here’s a quick table overview of these commands:
| Run Command | Description |
|---|---|
| cleanmgr | Opens Disk Cleanup |
| dxdiag | Opens DirectX Diagnostic Tool |
| eventvwr | Opens Event Viewer |
| gpedit.msc | Opens Group Policy Editor |
| perfmon.msc | Opens Performance Monitor |
| services.msc | Opens Services console |
| control schedtasks | Opens the Task Scheduler |
| diskpart | Opens Disk Partitioner |
| drvmgmt.msc | Opens Driver Manager |
| dfrgui | Opens Disk Defragmenter |
Let’s go into the details of some of these commands:
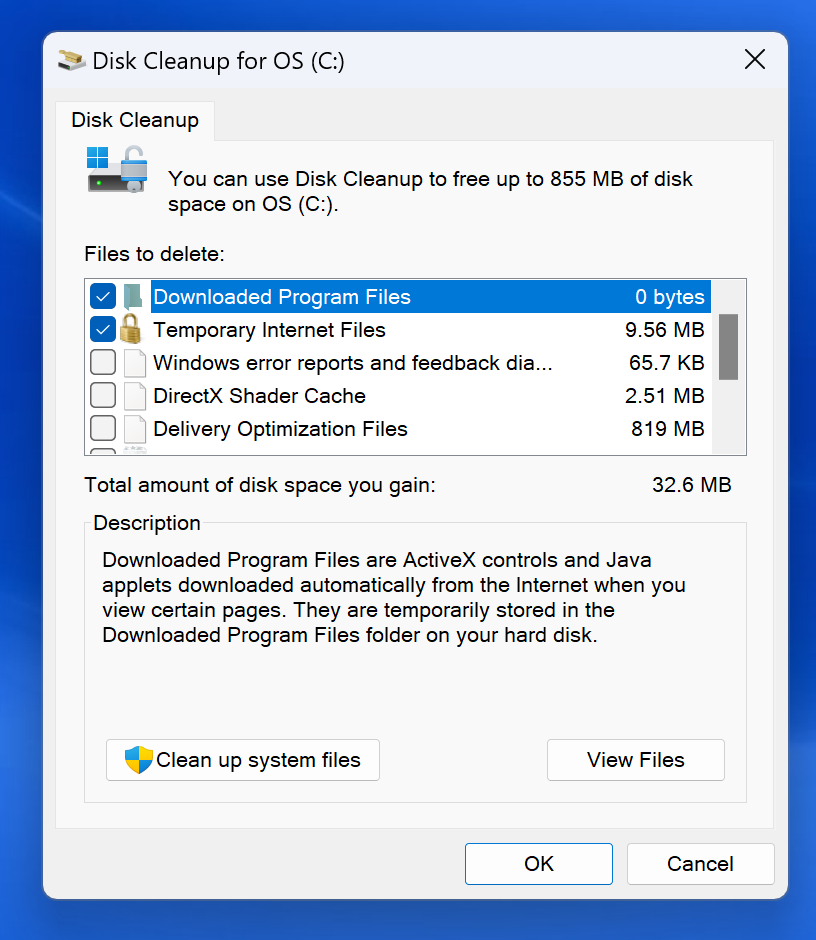
cleanmgr: Is your hard drive running out of space? ‘cleanmgr’ opens Disk Cleanup, a utility for removing unnecessary files from your hard drive, freeing up space and helping your computer run more efficiently.
dxdiag: If you’re experiencing issues with graphics or sound, or if you’re just curious about your system’s multimedia capabilities, ‘dxdiag’ opens the DirectX Diagnostic Tool. This tool provides detailed information about your system’s DirectX components and drivers.
eventvwr: To track down system problems or simply check up on your system’s health, use ‘eventvwr’ to open the Event Viewer. This tool logs detailed information about system events, such as errors, warnings, and informational events.
gpedit.msc: For advanced system administrators and power users, ‘gpedit.msc’ opens the Group Policy Editor, a powerful tool for managing the behavior of your system and network.
perfmon.msc: Are you a fan of performance data? ‘perfmon.msc’ opens the Performance Monitor, which provides detailed real-time information about your system’s hardware and software performance.
services.msc: This command opens the Services console, which provides a list of all services on your system, allowing you to manage them.
While these commands are powerful and can enhance your efficiency significantly. Understanding the implications of the actions these tools can perform is key to preventing unwanted changes or potential damage to your system.
Run Commands for Application Shortcuts
| Run Command | Description |
|---|---|
| osk | Opens On-Screen Keyboard |
| sndvol | Opens the volume mixer |
| charmap | Opens Character Map |
| utilman | Opens Ease of Access Center |
- osk: This command opens the On-Screen Keyboard, a virtual keyboard that you can use in place of a physical one. This feature is extremely useful when your actual keyboard is not functioning correctly or if you’re using a touch screen. It also helps in maintaining the security of your data as it can prevent keyloggers from tracking what you type.
- sndvol: Want to quickly access the volume mixer? The ‘sndvol’ command has got you covered. This tool lets you control the volume level for individual applications as well as the overall system sound. This comes in handy when you want to mute specific programs without affecting the entire system’s audio.
- charmap: The Character Map, opened by the ‘charmap’ command, is a utility that displays all characters of a selected font. It’s a lifesaver when you need to insert a special character that’s not on your keyboard. You can simply copy the needed character from the Character Map and paste it into your document.
- utilman: This command opens the Ease of Access Center, a tool that makes your PC easier to use. The center provides quick access to the settings for vision, hearing, and mobility. You can adjust settings like the screen magnifier, text-to-speech capabilities, and other accessibility features to customize your computer setup.
Run Commands for Troubleshooting Tools
| Run Command | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| msdt | Opens Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool | Read/Write |
| resmon | Opens Resource Monitor | Read Only |
| eventvwr.msc | Opens Event Viewer | Read Only |
| comexp.msc | Opens Component Services | Read/Write |
| odbcad32 | Opens ODBC Data Source Administrator | Read/Write |
| msconfig | Opens System Configuration | Read/Write |
| taskschd.msc | Opens Task Scheduler | Read/Write |
| verifier | Opens Driver Verifier Manager | Read/Write |
resmon: For a detailed overview of how your system’s resources are being used, type ‘resmon’ to open the Resource Monitor. This tool provides real-time data about CPU, disk, network, and memory usage.
msconfig: This command opens the System Configuration window, a hub for controlling your system’s startup process, services, and more. Remember, though, tinkering with these settings can have significant system-wide effects, so proceed with caution!
taskschd.msc: For advanced system task scheduling, use ‘taskschd.msc.’ It opens the Task Scheduler, a powerful tool that allows you to schedule the automatic execution of tasks at specific times or when certain conditions are met.
Run Commands for User Account Control
| Run Command | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| netplwiz | Opens User Accounts | Read/Write |
| lusrmgr.msc | Opens Local Users and Groups | Read/Write |
| control userpasswords2 | Opens User Accounts dialog box | Read/Write |
| credwiz | Opens Backup or Restore Wizard (Windows 7 and above) | Read/Write |
| secpol.msc | Opens Local Security Settings | Read/Write |
| gpedit.msc | Opens Group Policy Editor | Read/Write |
| control admintools | Opens Administrative Tools | Read/Write |
| azman.msc | Opens Authorization Manager | Read/Write |
| dsac.exe | Opens Active Directory Users and Computers | Read/Write |
Wrap-up
And just like that, we’ve reached the end of our journey through the labyrinth of Windows Run commands. We’ve seen how these simple commands, small in size but mighty in power, can completely transform the way we interact with our Windows systems. By cutting down on needless navigation and getting straight to the point, they make our work more efficient and our lives a bit easier.
Now that you’ve embarked on this tech exploration, why not share your experiences? Leave a comment below about how Windows Run commands have transformed your tech journey. Also, don’t forget to share this guide with fellow tech explorers. Together, we can navigate the vast digital universe more efficiently!